Most investors buy shares of their real estate investment trusts, or REITs (pronounced "reets") on public markets. However, not all REITs are of the publicly traded variety.
In fact, some public REITs are not traded on major exchanges, and some private REITs are not open to all investors and have few regulatory requirements.
Private REITs can be attractive for a few reasons. For one thing, they sometimes offer superior dividend yields to their publicly traded counterparts. Plus, their lower compliance costs have the potential to result in superior returns. However, there are several drawbacks to understand before you invest your own in a private REIT.

Types of REITs
Three types of REITs
Before we get into the pros and cons of private REITs, it's important to clarify that there are actually three types of REITs:
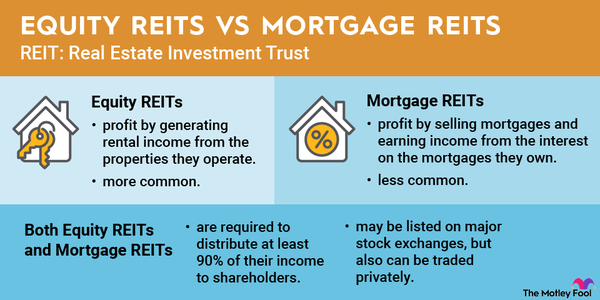
- Publicly traded REITs are what most people think of when they hear the term. These are the companies that are classified as REITs whose shares trade on major stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ. Mall REIT Simon Property Group (SPG 1.29%), logistics REIT Prologis (PLD 1.24%), and self-storage REIT Public Storage (PSA 1.36%) are some popular examples of publicly traded REITs. These companies trade just like ordinary stocks and are subject to the same regulatory compliance regulations as other publicly traded companies.
- Public non-listed REITs are available for investment to all U.S. investors, but their shares aren't listed on a major exchange. Most of the REITs offered by real estate crowdfunding platforms like RealtyMogul fall into this category. These REITs combine some of the features of publicly traded REITs and private REITs -- for example, they generally are illiquid, meaning their shares can't be readily traded, but they are subject to many of the same regulatory and investor protection requirements that apply to exchange-listed REITs. Some of the most well-known publicly traded REITs started out as public, non-listed REITs.
- Finally, private REITs are real estate investment trusts that are not listed on a major exchange and are not subject to most SEC regulatory requirements. Perhaps the most important thing to know about private REITs is that they are not available to all investors. They are generally sold by brokers and restrict investment to accredited and institutional investors to keep regulatory requirements low.
Advantages
Advantages of private REITs
While private REITs certainly aren't great investment choices for everyone, as we'll get into in the next section, there are several reasons why they could be attractive to investors:
- High dividend yields. Generally speaking, private REITs pay higher dividends than comparable public REITs. Public REITs have historically paid dividend yields in the 5% to 6% range, on average, while private REIT dividend yields have historically been in the 7% to 8% ballpark, according to National Real Estate Investor.
- No daily market fluctuations. Most private REITs only calculate their share prices every quarter, so investors don't need to stress about daily market fluctuations. If you find yourself obsessing over the share prices of stocks in your portfolio and worrying whenever one of your stocks goes down, the infrequent pricing updates of private REITs could be an attractive quality.
- Low compliance costs. Public REITs are required to comply with regular financial reporting and corporate governance rules, just like other public companies. This can be quite costly. Because they are subject to very few regulatory requirements, private REITs can save significant money in this area and can (theoretically) generate superior risk-adjusted returns when compared with their publicly-traded counterparts.
Drawbacks
Potential drawbacks of private REIT investing
With these advantages in mind, it's important to mention that there are several important disadvantages to investing in private REITs. Before you consider investing in a private REIT, here are some of the potential drawbacks you need to be familiar with:
- Lack of transparency -- Private REITs are not subject to the same regulatory scrutiny as public REITs, as they're exempt from SEC registration). As we saw in the last section, this can be a benefit, but it can also be a drawback. Because of the lack of regulation, private REIT managers have plenty of opportunities to make decisions that aren't necessarily in the best interest of shareholders. For example, conflicts of interest don't need to be disclosed by private REIT sponsors. It can also be hard to find any reliable performance data on private REITs as a whole. (In full disclosure, this is the number one reason I don't own any private REITs in my investment portfolio.)
- Accredited investors only. Because of the increased risks, the potential for investor abuse, and the lack of a liquid market, private REITs are available to accredited investors only. This generally means that they're restricted to institutional investors or individuals with at least $1 million in assets or income of at least $200,000 annually.
- Lack of liquidity. Once you invest in a private REIT, it can be difficult to cash out. Whereas publicly traded REITs allow you to sell shares instantly whenever the market is open, the same isn't true for private REITs. Each company has its own rules when it comes to the redemption of shares, and these can be very restrictive.
- High commissions (usually). Private REITs are often sold to investors by brokers. Therefore, a substantial portion of your private REIT investment could go toward commissions. In fact, there are reports of private REITs that pay as much as 12% in marketing fees and commissions. This means that if you invest $10,000 into a private REIT, as little as $8,800 of your money could actually end up being invested. While most private REIT fees aren't quite this high, it's important to be aware of them. After all, publicly traded REITs have no commissions involved other than the small trading commission charged by your brokerage.
- High minimum investments. Private REITs typically have minimum investments that range from $1,000 to $25,000 (or more in some cases). On the other hand, you can invest in a publicly traded REIT for the cost of one share, or even less if your broker allows fractional share trading.
Related investing topics
Should I invest?
Are private REITs right for you?
Here's my two cents on private REITs: In most cases, I feel that the drawbacks of private REIT investing outweigh the potential benefits. I've evaluated many private REITs, and I'd estimate that at least 90% of them charge what I consider excessive commissions and fees, especially when there are some excellent publicly traded alternatives. Plus, it's tough to find an investment strategy or potential return that justifies the lack of transparency and liquidity.
It's important to acknowledge that not all private REITs are inferior investments to their public counterparts. If you don't mind the lack of liquidity and find a private REIT opportunity that looks interesting, it's important to thoroughly read the investment's prospectus to find out exactly how much of your money will go toward fees and commissions. Also, check out the background of the REIT's management team and other key factors.
In short, when it comes to private REIT investing, the SEC and other regulatory agencies aren't going to have your back, so you'll need to protect yourself. If you have the time, knowledge, and desire to thoroughly evaluate private REIT investment opportunities on your own, it's entirely possible to find a diamond in the rough. If not, you're probably better off sticking with publicly traded REITs, which have high dividends and growth potential without the additional headaches.